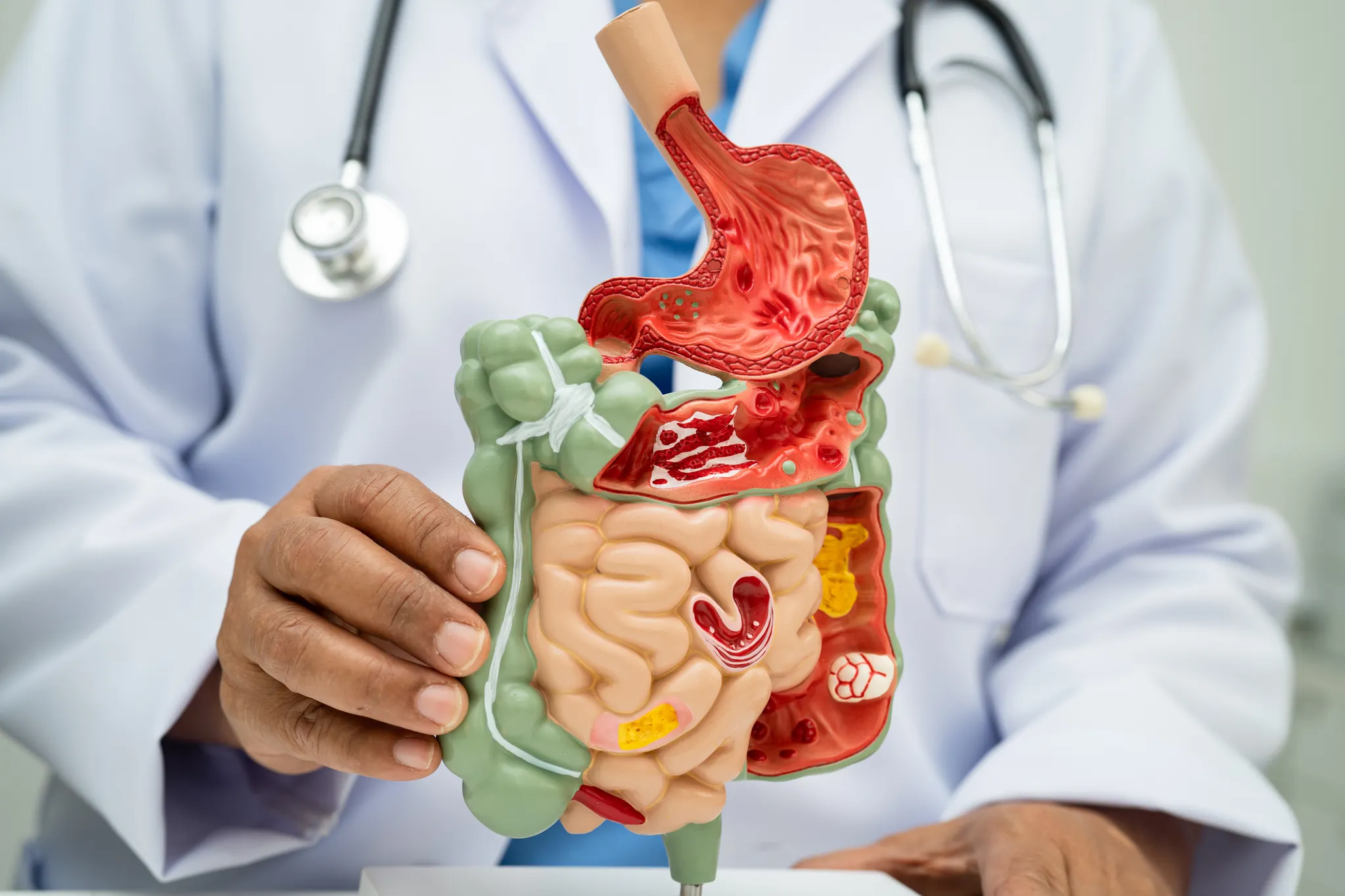
Digestion is the process of breaking down food into nutrients, while metabolism is how your body uses those nutrients for energy, growth, and repair. Understanding the distinction and their interplay can help optimise energy, weight management, and long-term health.
What Is Digestion?
Digestion is your body’s food processing system, breaking down food into usable compounds ready for absorption.
- It starts in the mouth, where chewing and saliva begin breaking down food.
- In the stomach, acids and enzymes continue the breakdown.
- In the intestines, nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream, and waste is prepared for elimination.
This is the extraction phase, converting meals into units like glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids, your body’s “fuel.”
⇒ ⇒ Read More – 7 Signs of Slow Metabolism in Females
What Is Metabolism?

Metabolism is the sum of all the chemical reactions your body performs to keep you alive and functioning.
It takes the nutrients released during digestion: glucose from carbohydrates, amino acids from proteins, fatty acids from fats, plus vitamins, minerals, and water and puts them to work.
- Catabolism: breaking down molecules (like glucose) to release energy for movement, breathing, and cellular activity.
- Anabolism: building and repairing tissues, creating hormones, and storing energy for future use.
These processes never stop. Whether you’re sleeping, thinking, exercising, or even healing a wound, metabolism is running in the background 24/7.
It fuels everything from hormone production and immune defence to muscle repair and brain function; essentially, it’s how your body turns nutrients into life.
⇒ ⇒ Read More – What is the Difference Between Fast & Slow Metabolism?
Digestion vs. Metabolism
| Feature | Digestion | Metabolism |
| What it does | Breaks food into nutrients | Uses nutrients for energy, repair, and storage |
| Where | Mouth, stomach, intestines | All body cells |
| Purpose | Fuel extraction | Fuel utilisation and body functioning |
| Timing | Occurs hours after eating | Continuous |
| Example | Breaking rice into glucose | Converting glucose into ATP (cellular energy) |
How They Work Together?
- Digestion is like the fuel depot. It supplies glucose and amino acids.
- Metabolism is your engine. It decides whether to burn, store, or use that fuel.
- If digestion is impaired, metabolism lacks quality fuel; if metabolism is sluggish, even good digestion won’t optimise energy use.
In India, where refined carbs and sedentary lifestyles are common, both processes often work under strain, contributing to rising rates of diabetes, fatty liver disease, and PCOS.
➔ ➔ Check out GoodFlip’s best diabetes care remission program, liver care remission program, PCOS remission program & weight management program.
⇒ ⇒ Read More – Is Papaya Good for Diabetes? Benefits, How to Eat It, and Smart Alternatives
How Digestion and Metabolism Interact?
Digestion provides the building blocks, and metabolism determines how effectively your body uses them. Hormonal signals (like insulin) regulate this synergy.
Efficient interplay ensures stable energy, weight control, and reduced risk of metabolic diseases.
8 Tips to Improve Both Digestion and Metabolism
- Eat Whole, Balanced Meals: Prioritise fibre-rich foods like whole grains, veggies, pulses, and lean protein. These support digestion and moderate blood sugar spikes for metabolism. The whole-food approach nurtures both systems.
Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water; it helps break down food, transport nutrients, and support digestive flow.
Move After Meals: A 10‑minute walk post-meal improves digestion by speeding gastric emptying, aids glucose absorption, and supports metabolic health; also improves circulation and mood.
Prioritise Sleep & Manage Stress: Stress slows digestion and disrupts metabolic hormones like insulin; better sleep helps maintain equilibrium.
Support Gut Health: Try probiotic-rich foods (yoghurt, dosa/Idli batter) and prebiotic fibres (garlic, onions, bananas). These feed beneficial gut bacteria, improving digestion and metabolic signalling.
Eat Slow & Mindfully: Chewing thoroughly aids digestion and signals fullness quickly, preventing overeating.
Include High-Fibre Indian Superfoods: Masoor dal, raw papaya, methi seeds, roasted chana, psyllium husk. These support both digestion and metabolism naturally.
Use Herbal Digestive Drinks: Simple infusions using ajwain/cumin, lemon + honey, or ACV tonic before meals can aid digestion and blood sugar control, supporting metabolism.
⇒ ⇒ Read More – How to Check if Your Metabolism is Damaged: Symptoms, Causes & Recovery (2025 Guide)
FAQs
1. Which matters more: digestion or metabolism?
They’re both essential. Digestion supplies the fuel; metabolism decides how it’s used. Weakness in either impacts energy, weight, and health.
2. Can improving digestion boost metabolism?
Yes. When digestion absorbs nutrients well, metabolism has quality fuel to work efficiently.
3. Natural ways to boost metabolism?
Build muscle, maintain activity, get enough protein, hydrate, sleep well, and manage stress.
4. Foods for better digestion?
Whole grains, leafy greens, low‑fructose fruits, avocados, fermented foods, adequate hydration. (Johns Hopkins)
5. Does water increase metabolism?
Modestly. It supports all metabolic functions and prevents sluggishness from dehydration.